ETFs and Mutual Funds: Understanding the Differences
Investors looking to diversify their portfolio often consider ETFs and mutual funds as viable options. Both types of investment vehicles offer a way to invest in a variety of assets, such as stocks, bonds, and commodities, without the need for individual security selection. However, there are some key differences between ETFs and mutual funds that investors should understand before making an investment decision.
What are ETFs?
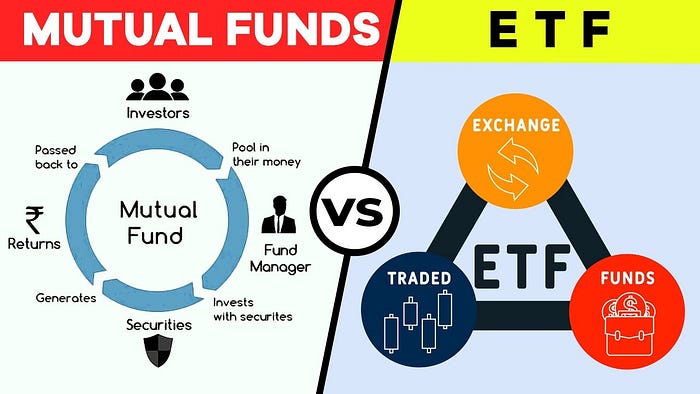
ETFs, or exchange-traded funds, are a type of investment vehicle that trades on a stock exchange like a stock. They are designed to track the performance of a particular index, such as the S&P 500 or the Nasdaq Composite. ETFs can hold a variety of assets, including stocks, bonds, and commodities, and are traded throughout the day at market prices.
One of the advantages of ETFs is their low cost. Since they are passively managed and track an index, they typically have lower fees than actively managed mutual funds. ETFs also offer tax efficiency, as they typically generate fewer capital gains than mutual funds.
Another advantage of ETFs is their flexibility. Since they trade like a stock, investors can buy and sell ETFs throughout the day, unlike mutual funds, which are priced at the end of the trading day. ETFs also allow investors to trade options, short-sell, and use margin, providing more advanced investment strategies.
What are Mutual Funds?
Mutual funds are a type of investment vehicle that pools money from multiple investors to purchase a diversified portfolio of stocks, bonds, and other securities. They are managed by a professional fund manager who actively selects securities to achieve the fund’s investment objective. Mutual funds are priced once per day, at the end of the trading day, based on the net asset value (NAV) of the fund.
One of the advantages of mutual funds is their professional management. Mutual fund managers have access to extensive research and resources to help them make informed investment decisions. Additionally, mutual funds offer diversification, as they invest in a variety of assets to minimize risk.
However, mutual funds often have higher fees than ETFs due to their active management. These fees can eat into an investor’s returns over time. Mutual funds are also less flexible than ETFs, as they can only be traded at the end of the trading day and do not offer options trading or short-selling.
Which is Right for You?
Deciding whether to invest in ETFs or mutual funds ultimately comes down to your investment goals and preferences. If you are looking for a low-cost, tax-efficient way to invest in a broad market index, ETFs may be the way to go. If you prefer professional management and a diversified portfolio, mutual funds may be a better choice.
It is also important to consider your investment strategy. If you are a long-term investor with a buy-and-hold strategy, either ETFs or mutual funds may be appropriate. However, if you are an active trader looking to make frequent trades, ETFs may be a better fit due to their flexibility and ability to trade throughout the day.
In conclusion, both ETFs and mutual funds offer investors a way to diversify their portfolios without the need for individual security selection. By understanding the differences between these investment vehicles, investors can make an informed decision about which one is right for their investment strategy and goals.
Do you want to To promote your business?
Get Your Business Featured at businessdor.com/get-featured/
Businessd’Or is a media company focused on business, innovation, investment, technology, entrepreneurship, leadership and lifestyle.