Difference Between CBD and CBG: A Comprehensive Guide
The world of cannabinoids is vast and complex, with over 100 different compounds found in the cannabis plant. Among these, CBD (cannabidiol) and CBG (cannabigerol) have garnered significant attention for their potential therapeutic benefits. While both are non-psychoactive and offer a range of health benefits, they differ in their effects, interactions with the body, and the way they are sourced and used. Understanding the differences between CBD and CBG is essential for anyone interested in the therapeutic potential of cannabis-derived compounds. This article explores the difference between CBD and CBG, their respective benefits, and how they can be used together to enhance overall well-being.
What is CBD?
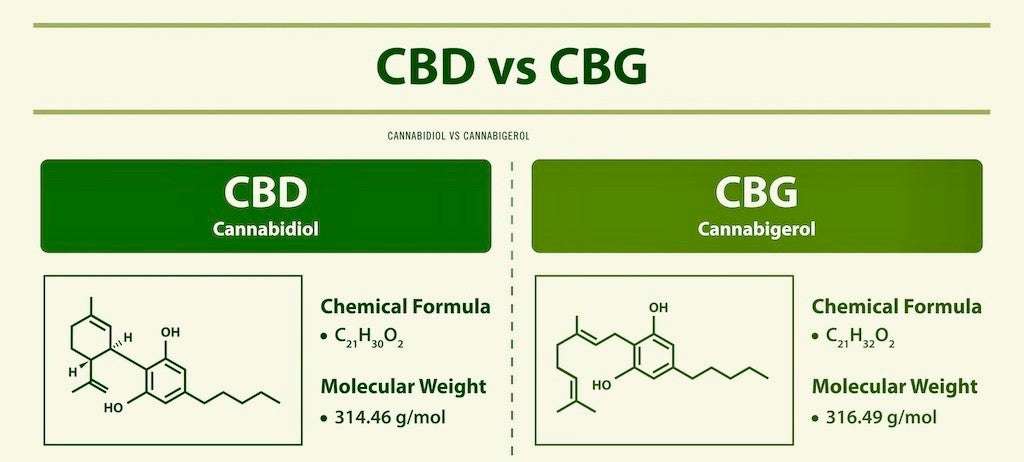
CBD, or cannabidiol, is one of the most well-known cannabinoids, second only to THC (tetrahydrocannabinol) in terms of popularity. Unlike THC, CBD does not have psychoactive properties, meaning it does not produce the “high” associated with marijuana use. This has made CBD a popular choice for individuals seeking relief from various health issues without the mind-altering effects of THC.
CBD is primarily extracted from hemp, a variety of cannabis that contains only trace amounts of THC. It interacts with the body’s endocannabinoid system (ECS), which plays a crucial role in regulating various physiological processes such as pain, mood, appetite, and sleep. CBD binds indirectly with cannabinoid receptors (CB1 and CB2) in the ECS, influencing these processes and promoting balance within the body.
What is CBG?
Another non-psychoactive cannabinoid included in the cannabis plant is called cannabigerol, or CBG. Often referred to as the “mother of all cannabinoids,” CBG is the precursor to other cannabinoids, including CBD and THC. In its acidic form, cannabigerolic acid (CBGA), CBG is the first cannabinoid produced by the cannabis plant. Through enzymatic reactions, CBGA is converted into CBDA (cannabidiolic acid) and THCA (tetrahydrocannabinolic acid), which are then decarboxylated to form CBD and THC, respectively.
Due to this conversion process, mature cannabis plants contain only small amounts of CBG, making it more difficult and expensive to extract in significant quantities. However, like CBD, CBG has shown promise in various therapeutic applications and is becoming increasingly popular in the wellness industry.
The Key Difference Between CBD and CBG
Difference between CBD and CBG share some similarities, they differ in several key areas, including their chemical structure, effects on the body, and potential health benefits.
1. Chemical Structure and Source
- CBD: CBD is typically found in higher concentrations in hemp plants. It is one of the primary cannabinoids in the plant and can be extracted relatively easily.
- CBG: CBG is present in much smaller quantities in mature cannabis plants, as most of it is converted into other cannabinoids. This makes CBG rarer and more challenging to extract. Breeders are developing cannabis strains with higher CBG content to make extraction more feasible.
2. Interaction with the Endocannabinoid System
- CBD: CBD interacts with the ECS by modulating the activity of the CB1 and CB2 receptors indirectly. It does not bind directly to these receptors but influences the ECS by increasing the levels of endocannabinoids in the body, such as anandamide, which helps regulate mood and pain.
- CBG: CBG, on the other hand, has a more direct interaction with the ECS. It binds directly to both CB1 and CB2 receptors, though it has a stronger affinity for CB2 receptors. This direct interaction allows CBG to potentially have more targeted effects, particularly in areas related to inflammation and pain.
3. Therapeutic Benefits
- CBD: CBD is widely known for its potential in managing anxiety, depression, chronic pain, and epilepsy. Epidiolex, a medication based on CBD, has received FDA approval to treat specific forms of epilepsy. Additionally, CBD has anti-inflammatory, antioxidant, and neuroprotective properties, making it a popular choice for a wide range of health concerns.
- CBG: CBG is gaining recognition for its potential in treating conditions such as glaucoma, inflammatory bowel disease (IBD), and certain types of cancer. It has strong antibacterial properties, particularly against antibiotic-resistant bacteria like MRSA (methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus). CBG also shows promise in supporting brain health and protecting neurons, which could be beneficial in neurodegenerative diseases.
4. Psychoactivity and Safety
- CBD: CBD is non-psychoactive and generally considered safe for use in a variety of populations, including children and the elderly. It has a well-established safety profile with few side effects, which are usually mild and include dry mouth, drowsiness, and changes in appetite.
- CBG: Like CBD, CBG is also non-psychoactive and considered safe. However, due to its lower availability and shorter history of use, there is less research on its long-term safety and potential side effects. Early studies suggest that CBG is well-tolerated, but more research is needed to fully understand its safety profile.
How to Use CBD and CBG Together
One of the exciting possibilities in the world of cannabinoids is the concept of the “entourage effect,” where different cannabinoids work together to enhance each other’s effects. Using CBD and CBG together may provide a more comprehensive approach to wellness by targeting different aspects of health.
- CBD and CBG for Pain Relief: Combining CBD and CBG may enhance pain relief due to their complementary mechanisms of action. While CBD modulates the ECS to reduce pain perception, CBG’s direct interaction with CB2 receptors can further reduce inflammation, offering a more robust pain management strategy.
- CBD and CBG for Anxiety and Stress: CBD is well-known for its calming effects, and CBG may contribute to these effects by supporting overall mental clarity and focus. Together, they can help manage anxiety and stress more effectively than either compound alone.
- CBD and CBG for Neuroprotection: Both CBD and CBG have neuroprotective properties, making their combination potentially beneficial for those with neurodegenerative diseases or those looking to support brain health as they age.
The Future of CBD and CBG
As research into cannabinoids continues, CBD and CBG will likely play increasingly important roles in the wellness industry. Advances in cultivation and extraction techniques may make CBG more accessible, allowing its benefits to be more widely studied and utilized. Additionally, as more people become aware of the differences between CBD and CBG, we expect to see more products combining these cannabinoids to offer a more holistic approach to health and wellness.
Conclusion
Difference between CBD and CBG share similarities as non-psychoactive cannabinoids with therapeutic potential, they differ in their sources, mechanisms of action, and specific health benefits. CBD is well-established in the wellness community, known for its ability to manage anxiety, pain, and inflammation, while CBG is emerging as a powerful cannabinoid with unique properties, particularly in areas like neuroprotection and antibacterial activity. Understanding the difference between CBD and CBG allows consumers to make more informed decisions about how to incorporate these cannabinoids into their wellness routines, whether individually or in combination, to achieve optimal health outcomes.